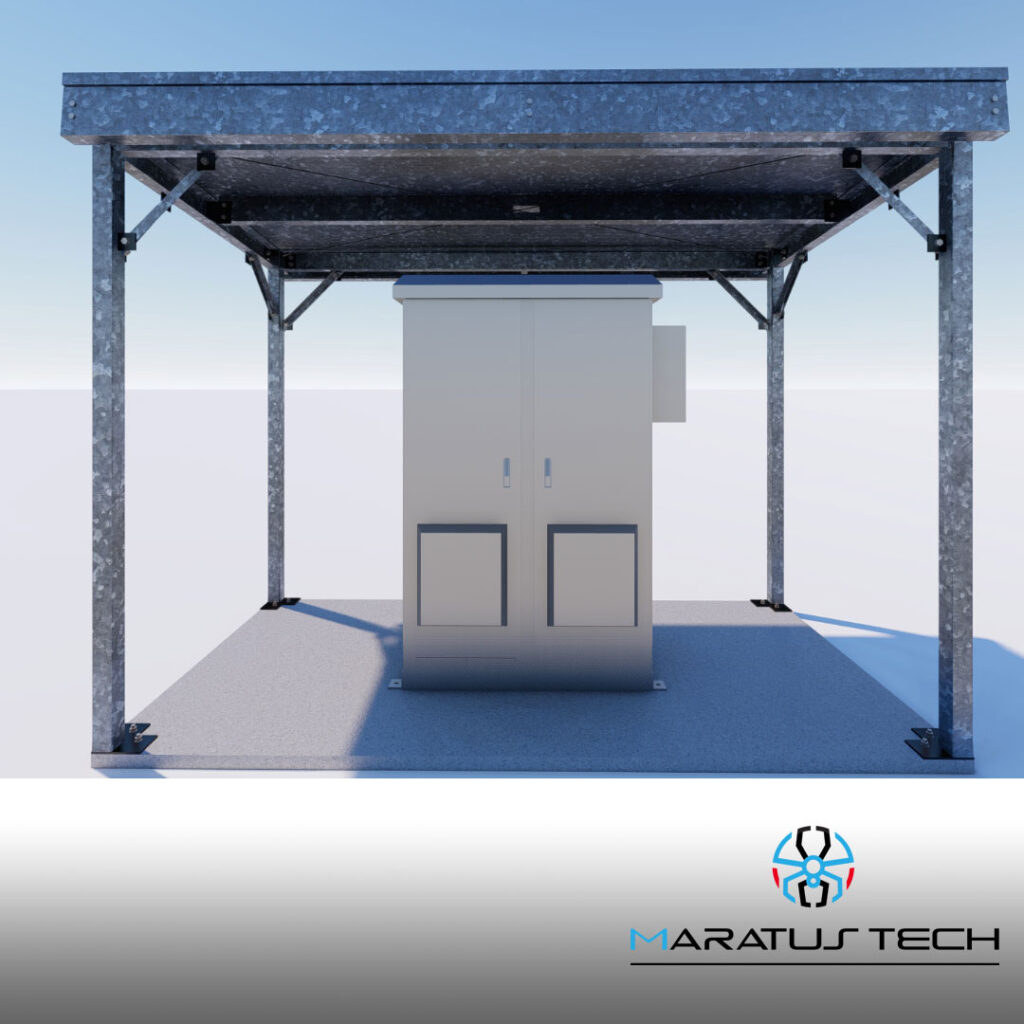
Telco shelters are essential for housing telecommunications equipment, providing protection from environmental elements and ensuring the reliability of network operations. This guide covers the fundamental aspects of designing telco shelters, including structural requirements, environmental considerations, and material choices to ensure optimal performance.
Key Considerations in Telco Shelter Design
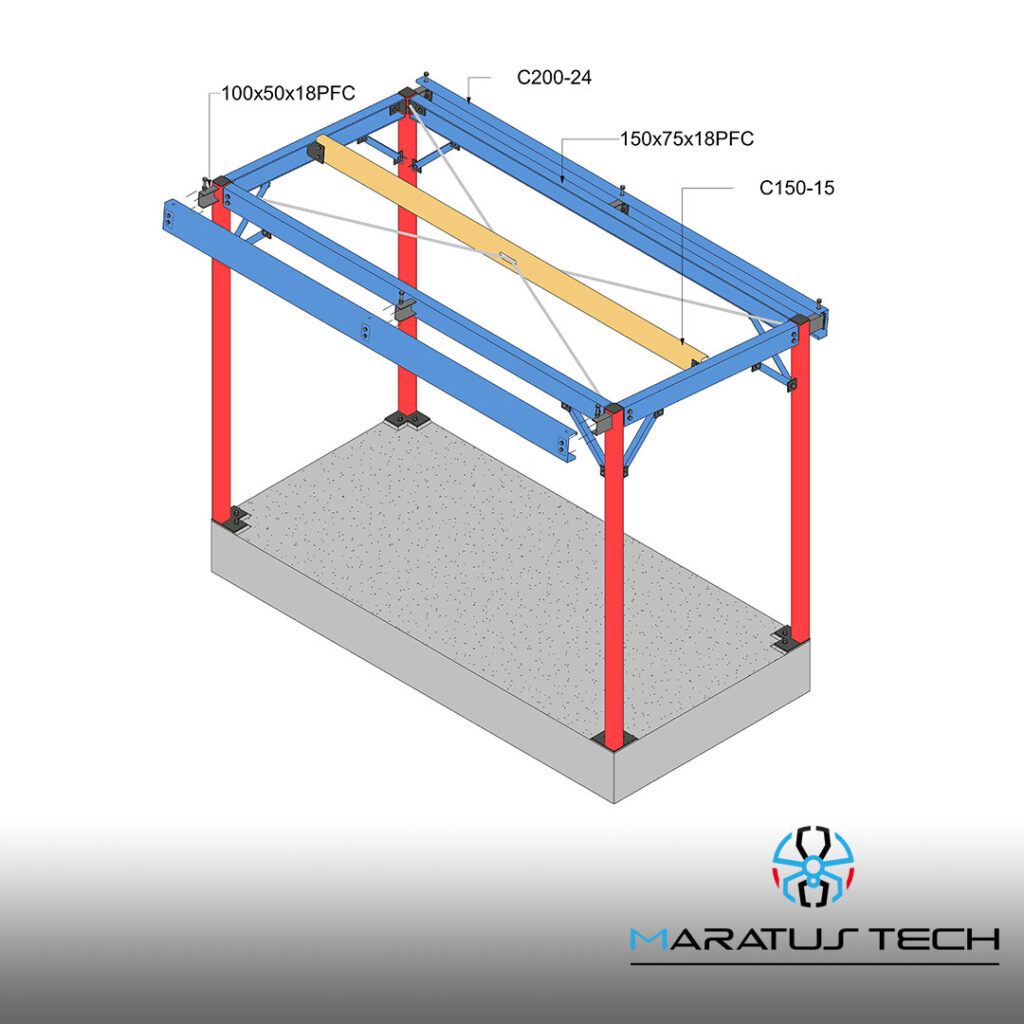
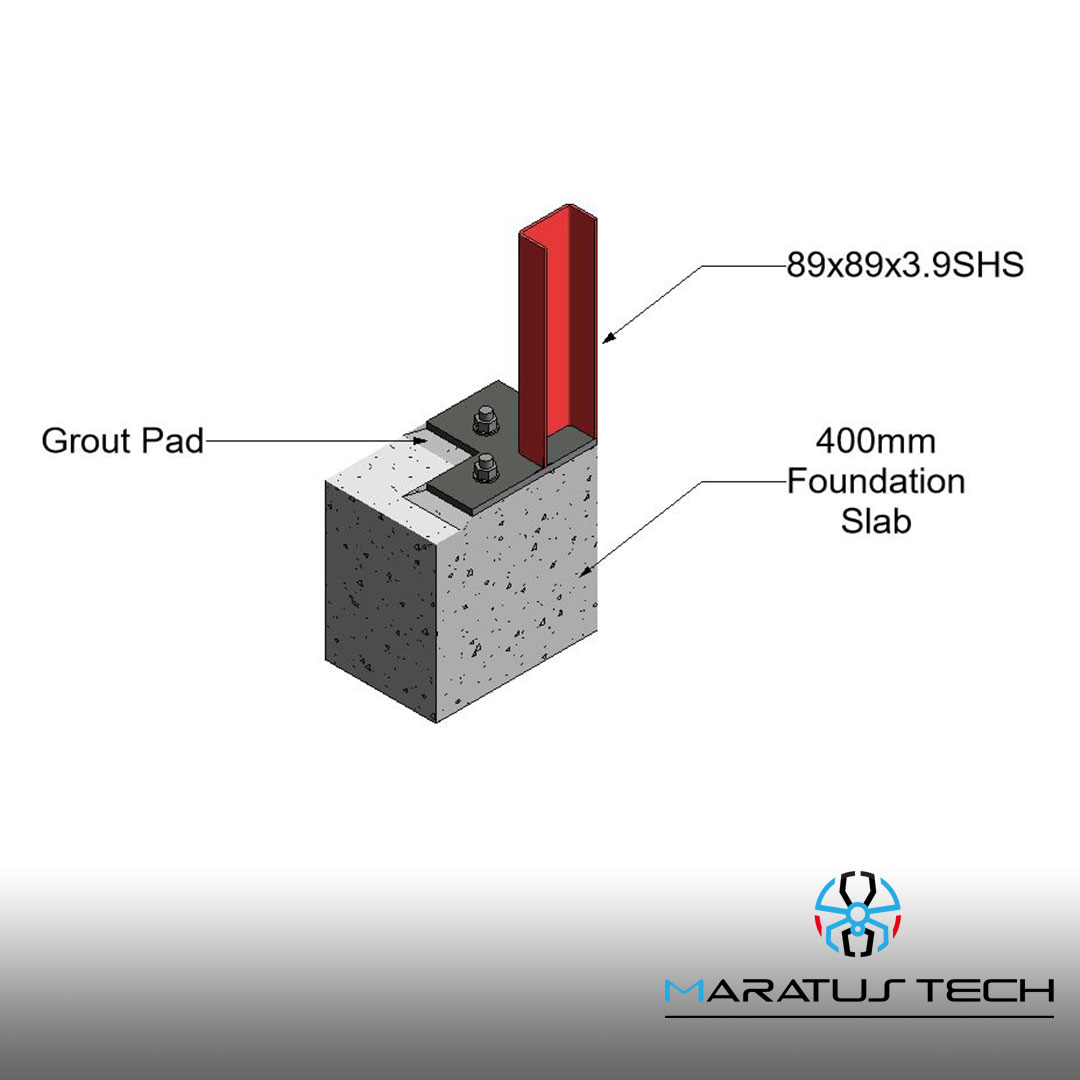
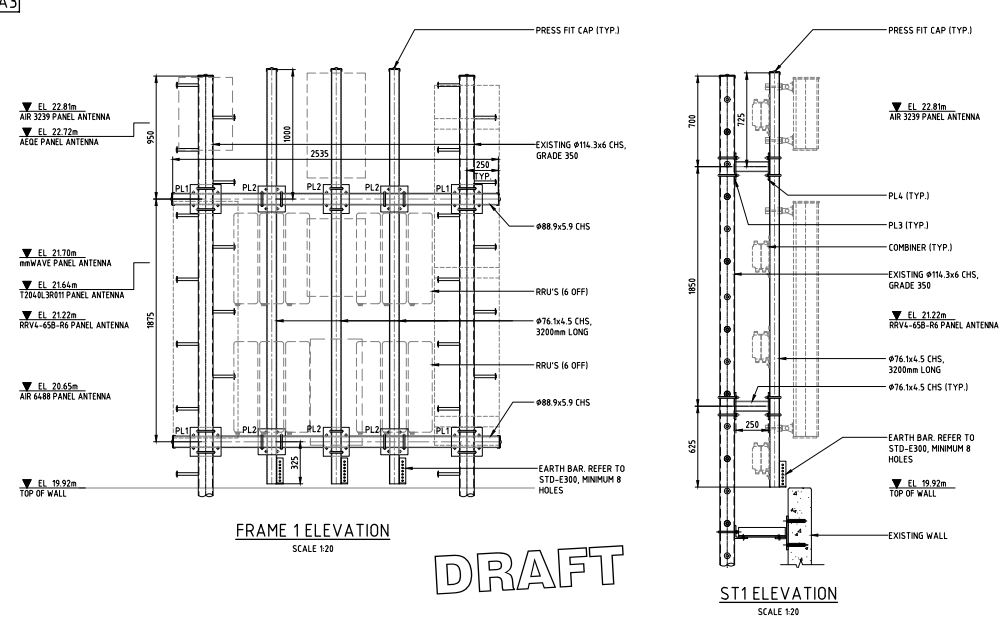
1. Structural Requirements:
- Load-Bearing Capacity: Ensure the shelter can support the weight of telecom equipment and any additional loads such as snow or wind.
- Seismic Resistance: Design the structure to withstand seismic activities, especially in earthquake-prone areas.
- Wind Resistance: Evaluate the shelter’s ability to resist high winds and protect the equipment inside.
2. Environmental Factors:
- Climate Conditions: Consider the local climate, including temperature extremes, humidity, and precipitation, to ensure proper insulation and ventilation.
- Protection Against Elements: Ensure the shelter provides adequate protection against rain, snow, dust, and other environmental elements.
3. Material Choices:
- Durability: Select materials that offer durability and long-term performance, such as galvanized steel, aluminum, or reinforced concrete.
- Thermal Insulation: Use materials with good thermal insulation properties to maintain stable internal temperatures and reduce energy consumption.
- Corrosion Resistance: Choose materials that are resistant to corrosion, especially in coastal or industrial areas where corrosive elements are prevalent.
Best Practices for Telco Shelter Design
1. Site Assessment:
- Conduct a thorough site assessment to understand the environmental conditions and specific requirements of the location.
- Ensure the site is accessible for maintenance and installation activities.
2. Modular Design:
- Consider a modular design approach for flexibility and scalability. Modular shelters can be easily expanded or reconfigured as needed.
3. Efficient Layout:
- Plan the internal layout to optimize space utilization and ensure easy access to equipment for maintenance and upgrades.
- Include pathways for cabling and ventilation to prevent clutter and ensure efficient airflow.
4. Ventilation and Cooling:
- Implement effective ventilation and cooling systems to prevent overheating of equipment. Options include air conditioning units, ventilation fans, and passive cooling techniques.
5. Security Features:
- Incorporate security features such as robust locks, surveillance cameras, and alarm systems to protect the shelter and its contents from theft and vandalism.
6. Power Supply and Backup:
- Ensure a reliable power supply with backup options such as generators and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) to maintain continuous operation during power outages.
7. Compliance with Standards:
- Adhere to relevant industry standards and regulations to ensure the shelter meets safety and performance criteria.
Conclusion
Designing a telco shelter involves careful consideration of structural requirements, environmental factors, and material choices. By following the best practices outlined in this guide, telecom operators can create robust and reliable shelters that protect their equipment and ensure uninterrupted network operations.