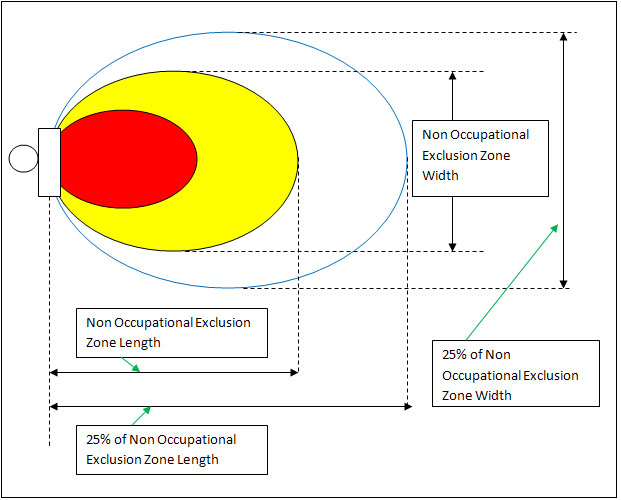
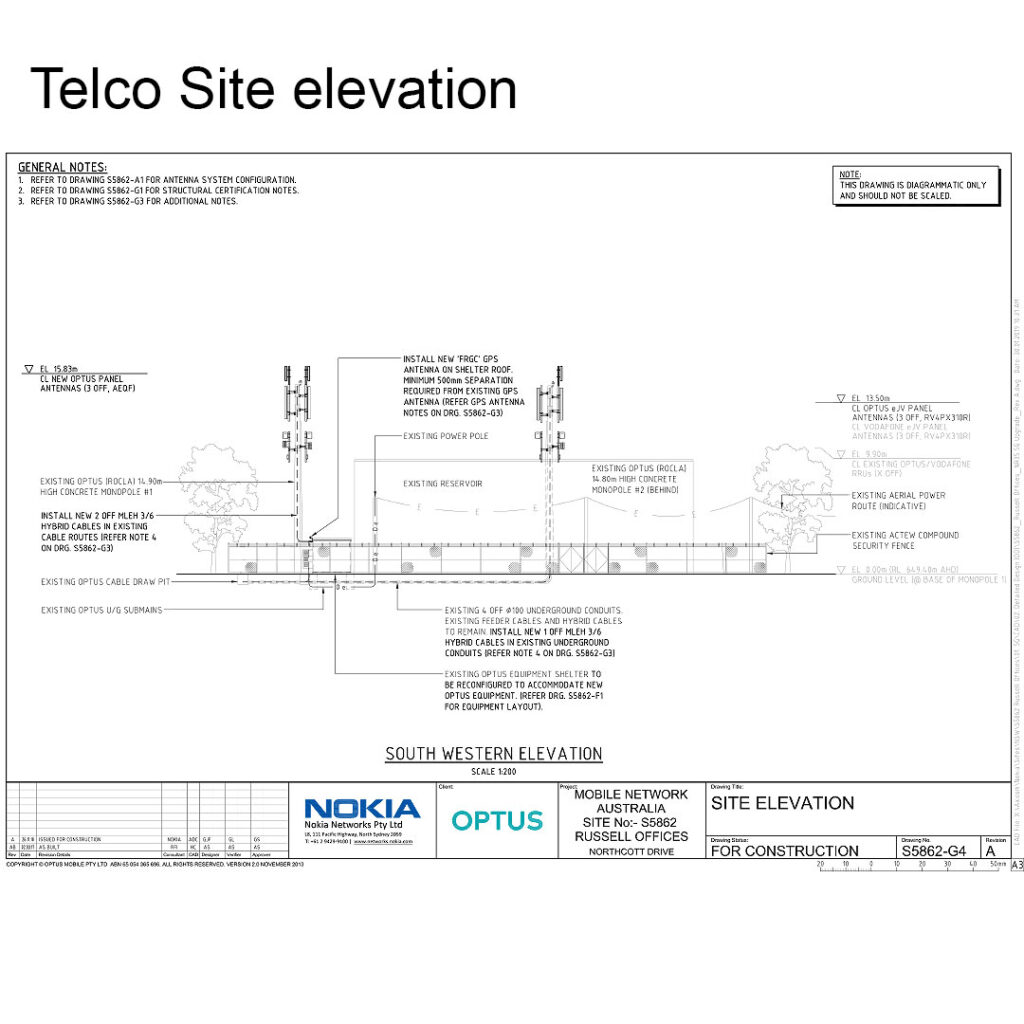
Power equipment is a critical component of telecom sites, ensuring that all systems run smoothly and without interruption. This guide provides an overview of essential power equipment used in telecom sites, discussing their functions, benefits, and best practices for ensuring a reliable and efficient power supply.
Key Power Equipment for Telecom Sites
1. Generators:
- Purpose: Provide backup power during outages to maintain continuous operation of telecom systems.
- Types: Diesel generators, natural gas generators, and renewable energy generators.
- Benefits: Reliable power supply, long runtime, and scalability.
2. Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS):
- Purpose: Offer short-term power backup and protection against power surges and interruptions.
- Types: Standby UPS, Line-Interactive UPS, and Online UPS.
- Benefits: Protect sensitive equipment, reduce downtime, and improve system reliability.
3. Batteries:
- Purpose: Store energy for use during power outages or fluctuations.
- Types: Lead-acid batteries, Lithium-ion batteries, and Nickel-cadmium batteries.
- Benefits: High energy density, long life span, and low maintenance.
4. Power Distribution Units (PDUs):
- Purpose: Distribute electrical power to various components within the telecom site.
- Types: Basic PDUs, Metered PDUs, and Switched PDUs.
- Benefits: Efficient power distribution, remote monitoring, and enhanced control.
5. Rectifiers:
- Purpose: Convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) to power telecom equipment.
- Benefits: High efficiency, compact design, and improved power quality.
6. Inverters:
- Purpose: Convert DC power from batteries or other sources into AC power.
- Benefits: Ensure continuous power supply, support various loads, and enhance flexibility.
7. Surge Protectors:
- Purpose: Protect telecom equipment from voltage spikes and electrical surges.
- Benefits: Prevent damage to equipment, increase system lifespan, and improve safety.
8. Cooling Systems:
- Purpose: Maintain optimal operating temperatures for power equipment and telecom systems.
- Types: Air conditioning units, ventilation systems, and liquid cooling systems.
- Benefits: Prevent overheating, improve efficiency, and reduce energy consumption.
Best Practices for Power Equipment Management
1. Regular Maintenance:
- Routine Inspections: Conduct regular inspections and maintenance of power equipment to ensure optimal performance.
- Preventive Measures: Implement preventive measures to identify and address potential issues before they cause downtime.
2. Redundancy Planning:
- Backup Systems: Install backup power systems, such as generators and UPS, to ensure continuous operation during power outages.
- Redundant Components: Use redundant components to minimize the impact of equipment failures.
3. Energy Efficiency:
- Efficient Equipment: Choose energy-efficient power equipment to reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
- Power Management: Implement power management strategies to optimize energy usage and reduce waste.
4. Monitoring and Control:
- Remote Monitoring: Use remote monitoring tools to track power equipment performance and detect issues in real-time.
- Automation: Automate power management processes to improve efficiency and reduce the risk of human error.
5. Compliance and Safety:
- Regulatory Standards: Ensure all power equipment complies with relevant regulatory standards and guidelines.
- Safety Protocols: Implement safety protocols to protect personnel and equipment from electrical hazards.
Conclusion
Ensuring a reliable and efficient power supply is essential for the smooth operation of telecom sites. By understanding the key power equipment and best practices for power management outlined in this guide, telecom operators can optimize their infrastructure and provide better services to their customers.